Assessing the Effects of ManyChat on Social Media Engagement Metrics: A Case Study of MaeMagan Blogsite Using Chatbot on Facebook
- Sep 7, 2025
- 30 min read
Updated: Sep 9, 2025

I wrote this capstone project as a requirement for my candidacy for Cum Laude Latin Honors. It was submitted to the Capstone Review Committee of ACE-RE Gardner College in Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines, on August 6, 2025. Today, September 7, 2025, is exactly a day before my graduation day. Unfortunately, I was informed by the school staff that I am disqualified from receiving Summa Cum Laude and Magna Cum Laude Latin Honors due to the following reasons:
(1) Having less than 10 years of work experience as a real estate broker. The main reason why students enroll in a Bachelor of Science in Real Estate Management (REM) is to take board exams for appraiser, broker, and consultant after graduation. As far as I am concern, academic institutions are established to train the students to develop certain knowledge and skills that will equipped them with strength and capabilities they need to perform their duties and responsibilities in their chosen career. Therefore, all graduating students who are qualified for Cum Laude Latin Honors should be evaluated purely based on their school performance such as the final grades on quizzes, assignments, oral presentation, and the capstone project submitted to the Capstone Review Committee. Do you think it is proper for the school leaders to set a criteria that limits the awarding of Summa Cum Laude and Magna Cum Laude only to those BS-REM students with more than 10 years of work experience in real estate industry?
Furthermore, students who are enrolled in educational institutions are there to learn. Students did not go to school to apply for a job. Thus, clearly, there is really a fine line that separates academic achievements from professional or work experience. You see, at the age of 48, BS-REM is already my third bachelors degree on top of my masters degree in Applied Business Economics. On top of my formal educational background, I spent 18 years as freelance ghost writer doing full-time research and writing service on various academic subjects. Working from Mondays to Sundays, I managed to complete 3,500+ orders all throughout 18 years I worked as a freelance ghost writer. Out of the 3,500+ orders, I have already lost count as to how many masters degree thesis and PhD thesis I have written and submitted to different well-known universities worldwide, including Harvard University, Oxford University, Cambridge University, and so on. It even came to a point that I got bored with my job as a freelance ghost writer and have tried to submit a computer-generated copy of my work schedule that reflects how many orders I can complete each day including some of the most complicated work I had written to Harvard University as my job application for the post of research assistant. The only reason my application was rejected was due to lack of sponsor to work in the United States.
To cut the story short, before anyone can work as a professional nurse, completing BS-Nursing and passing the board exam is a requirement. The same is true in legal profession. Before anyone can work as a professional lawyer, completing BS-Law and passing the Bar exam is a requirement. In the Philippines real estate industry, I understand that for a certain period of time, the "grandfather clause" in the RESA law --- also known as the Republic Act 9646 states that all individuals with the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) license can receive a Professional Regulation Commission (PRC) license without the need to take the real estate broker licensure examination. Starting in 2016, the CHED stated that only individuals who are graduates of a four-year BS-REM course are allowed to take licensure exam for appraisers, brokers, and consultants. The problem with having a school criteria that limits the awarding of Summa Cum Laude and Magna Cum Laude only to those BS-REM students with more than 10 years of work experience in real estate industry as professional brokers is discrimination to all students who are new players in the Philippine real estate industry. Likewise, such criteria may also trigger school politics and undermine a fair evaluation of the students' academic accomplishments in favor to those who have been active in the real estate industry 10, 15, or 20 years ago. In this context, Cum Laude Latin Honors should be awarded only based on the students' academic performance.
(2) Failure to participate in Face-to-Face class. During the graduation party which was held at Seda Vertis North between 7 p.m. to 11 p.m., I was quietly observing the face of Doctor Eduardo G. Ong as he was congratulating the lady who received the Magna Cum Laude honors. I noticed that both of them were quite close to each other. Suddenly, I remembered that after completing my second term in school, the school staff convinced me to immediately enroll in the online review for board exam even though I was in the process of enrolling for the third term. I even asked the school staff several times if the schedule for online review and other subjects I enrolled in the third semester would be a conflict. The school staff reassured me that there will not be a problem. Two days before graduation, failure to participate in the Face-to-Face class was also used against me.
On the graduation day, I had the opportunity to speak with a student who received both the leadership award and Cum Laude honors. I asked her about the face-to-face classes. Only then did she explain that BS-REM graduating students were assigned to participate in group activities such as interviews and writing a thesis on their chosen topic. She seemed puzzled since I knew nothing about the face-to-face classes. Then, she asked me if I was assigned to a group to write a thesis as required by CHED. I said, "No". However, almost a month before the graduation, 13 students in our batch were called to write a Capstone Research as part of the requirements for our candidacy for Cum Laude Latin Honors. The structure of a Capstone Research is similar to that of a thesis. So I told her that I had written and submitted my thesis on my own.
(3) Failure to complete 300-hours OJT as required by CHED. The school staff also questioned my 300-hours OJT as required by CHED. During my one-on-one online interview with Doctor E.G. Ong, I remembered that he instructed me to write 2 real-life case scenarios involving real estate transaction with ethical violations and write its corresponding solution. I always keep a copy of things they require me to submit. Since I felt a strong need to defend my candidacy for Cum Laude Latin Honors, I intentionally wrote an e-mail to the school. In one of my emails, I re-submitted the case study in PDF format thinking they may have overlooked what I submitted to them on March 13, 2025.
Thinking that the case study submission required by Doctor E.G. Ong did not suffice the 300-hours OJT required by CHED, I emailed the school declaring that I also worked under the supervision of an independent licensed broker who mentored me on how to secure the certified true copy of title from the Registry of Deeds, including tax declaration from the Assessor's office, conducting due diligence before property sales, managing titles with encumbrance or adverse claims, paying transfer fees, documentary stamp taxes, and 6% Capital Gain Tax (CGT), securing tax clearances, paying village dues, and preparing deed of absolute sale (DOAS). I also learned when to secure the certificate of affidavit of no claim, among other things. Together with the licensed broker's team, we were actively conducting site visits of properties for sale within and outside of Metro Manila (e.g., Makati, Pasay, Pasig, Tanay Rizal, Cavinti Laguna, Calamba Laguna, Tagaytay, and Batangas).
On top of regular field work with the independent broker, I am also active in managing and maintaining my own website as I engaged in online marketing activities which is not limited to updating website information, applying SEO techniques, integrating AI in digital marketing, editing of photos and videos, creating new video content, and responding to clients' inquiries since December 2022. I usually work from Mondays to Sundays, except when I need to do some self-care activities. Consequently, the time I spent on real estate-related work far exceeds the 300-hours required by CHED for OJT.

The school disqualified me from Summa Cum Laude and Magna Cum Laude honors for not having more than 10 years of work experience as a broker, failure to participate in the face-to-face class, and not complying with the 300-hours OJT as required by CHED. Instead, the school leaders congratulated me on receiving the Academic Excellence Award.
Despite the perceived unfairness of judgement from the Capstone Review Committee of ACE-RE Gardner College, I would like to share the official results of my study with the world. Upon investigating the impact of ManyChat on Facebook marketing performance of MaeMagan Blogsite, results of the quasi-experimental time series study shows that ManyChat contributed to an 8.6% increase in daily views, higher engagement through comments and reactions, and a rise in messaging conversations and followers. However, minimal impact was observed on post shares, suggesting that content quality plays a larger role in shareability. Overall, this capstone study concludes that chatbot automation is a strategic tool for real estate marketers who are seeking to scale their digital presence worldwide.
1. INTRODUCTION
Investing in online marketing --- also known as digital marketing --- is a strategic way to reach a wider audience in the real estate business (Meghashilpa & Suresh, 2024). However, establishing global visibility for a newly developed website remains a challenge. As Quesenberry (2024) pointed out, creating a blueprint for innovative change is essential to complement traditional marketing techniques such as print ads or newspaper ads. To help position MaeMagan Real Estate Blogsite as a global real estate brand, I developed a push marketing strategy utilizing social media platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok. By creating attractive and engaging video advertisements, I was able to promote rental and for-sale properties more effectively while applying a personalized approach in my public relations (PR) efforts with the target audience.
My long-term professional goal in real estate is to become a globally recognized online real estate marketer who provides free digital marketing services to property owners in Metro Manila. A chatbot uses natural language processing (NLP) and generative AI to analyze user input and generate human-like responses (IBM, 2021). Today, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, particularly chatbots that automate responses to social media posts, is rapidly increasing (Haleem et al., 2022; Grandinetti, 2023). As part of my creative works and self-learning experience, ManyChat (manychat.com) was integrated as the official chatbot of MaeMagan Blogsite's current video ad posts on Facebook.
In the field of social media advertising, Facebook marketers should closely monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as views, engagement (i.e., comments and replies, reactions, and shares), messaging conversations, and the number of followers. This study aims to compare daily and average Facebook post views, engagement, messaging conversations, and follower growth across two clearly defined time periods: before and after the implementation of ManyChat intervention. Therefore, the most appropriate research method for this capstone project is a quasi-experimental time series design. Using this method, the researcher was able to carefully examine and observe the extent to which ManyChat’s automated responses to post comments influenced Facebook’s KPIs on MaeMagan Blogsite’s most recent video ads and picture posts.
1.1 Purpose of the Study
MaeMagan Blogsite is a fast-growing content platform on Facebook. Using its most recent video ads and picture posts, this capstone project aims to determine the impact of using ManyChat’s automated response to post comments on Facebook’s KPIs such as views, engagement, messaging conversations, and the number of followers over two consecutive 10-day periods.
1.2 Problem Statement and Research Questions
1.2.1 Problem Statement
In today’s competitive digital marketing landscape, online marketers constantly seek new tools to enhance their online presence and user engagement. MaeMagan Blogsite has recently integrated ManyChat to automate and optimize its online posts communication strategy for online posts. However, it remains unclear how this integration may influence Facebook’s KPIs such as views, post engagement, messaging conversations, and followers’ growth. In the absence of empirical evidence, the effectiveness of using ManyChat’s automated responses to post comments on Facebook’s posts’ performance remains uncertain. By analyzing the most recent video ads and picture posts of MaeMagan Blogsite, this capstone project aims to help address this gap.
1.2.2 Research Questions
The main research question addressed in this capstone project is:
“What patterns or trends can be observed in Facebook KPI’s before and after the integration of ManyChat’s automated responses to post comments in MaeMagan Blogsite’s marketing strategy?”
Accordingly, the following sub-research questions will guide the investigation:
(1) How has the integration of ManyChat’s automated response to post comments influenced the number of views on MaeMagan Blogsite’s recent video ads and picture posts on Facebook?
(2) What impact has ManyChat’s automated response to post comments had on user engagement (i.e., likes, comments, shares, and reactions) with MaeMagan’s videos and picture post content?
(3) To what extent has the use of ManyChat’s automated response to post comments affected the volume and quality of messaging conversations initiated through Facebook?
(4) Has the implementation of ManyChat’s automated response to post comments contributed to an increase in the number of followers on MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook page?
1.3 Scope and Significance of the Study
1.3.1 Scope of the Study
This study focuses on evaluating the impact of ManyChat’s automated response to post comments on the performance of MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook page. The analysis will be limited to video ads and picture posts published at least ten (10) days before and after the integration of ManyChat. Additionally, four (4) key Facebook KPIs---views, engagement, messaging conversations, and the number of followers will be examined. Therefore, only data collected from MaeMagan Blogsite’s official Facebook page will be included in the actual data-gathering process.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Using 334 Vietnamese respondents to investigate the impact of chatbot on customer-brand relationships, customer response, and communication quality, Vo and Nguyen (2022) found out that the use of chatbot marketing efforts can improve communication quality in terms of accuracy, credibility, and competence. This is attributed to factors such as customization, entertainment, accessibility, information, and interaction. With improved communication quality serving as a mediating factor, Vo and Nguyen (2022) concluded that chatbox use is effective in terms of strengthening user response behavior and establishing customer-brand relationship.
Supporting these findings, Magno and Dossena (2023) showed through PLS-SEM analysis of an Italian consumer survey that both utilitarian and hedonic attributes of a chatbot positively affect long-term brand affinity and customer satisfaction. Their study also indicated that favorable brand attitudes formed through chatbot interactions may increase followers’ retention and engagement over time.
Contrary to these positive findings, Illescas-Manzano et al. (2021) argued that some people may reject chatbots due to lack of personalized attention or inaccurate responses to queries. To overcome such limitations, Cheng et al. (2021) suggested that using a friendly tone in chatbot interactions can enhance customers’ trust and willingness to reuse the chatbot, thereby improving brand perception.
In a scenario-based experiment comparing formal and informal language styles, Li and Wang (2023) revealed that informal or casual language use in chatbots may boost customers’ willingness to engage, influenced by parasocial interaction effects. Further, Xu et al. (2023), in their study on WeChat post characteristics, found that vibrant images and engaging video content significantly increase likes and shares. In this context, integrating ManyChat-prompted call-to-actions (CTAs) such as “Add-to-Cart” buttons, Messenger chat options, free trial sign-up prompts---could potentially drive higher views and engagement (Keenan, 2022).
Makad (n.d.) presented a six-stage sales funnel with corresponding pipeline stages, as illustrated in Figure 1. According to Makad (n.d.), marketers must first create public awareness before reaching discovery stage, where lead generation becomes possible. Without qualifying leads, closing a sale is unlikely. Supporting this, Illescas-Manzano et al. (2021) found out that using the ManyChat platform on Facebook Messenger, compared to other chatbot tools, can positively impact lead capture due to enhance two-way communication between marketers and their audience. (See Figure 1.1 – Sales Funnel Stages with Its Corresponding Pipeline Stages)
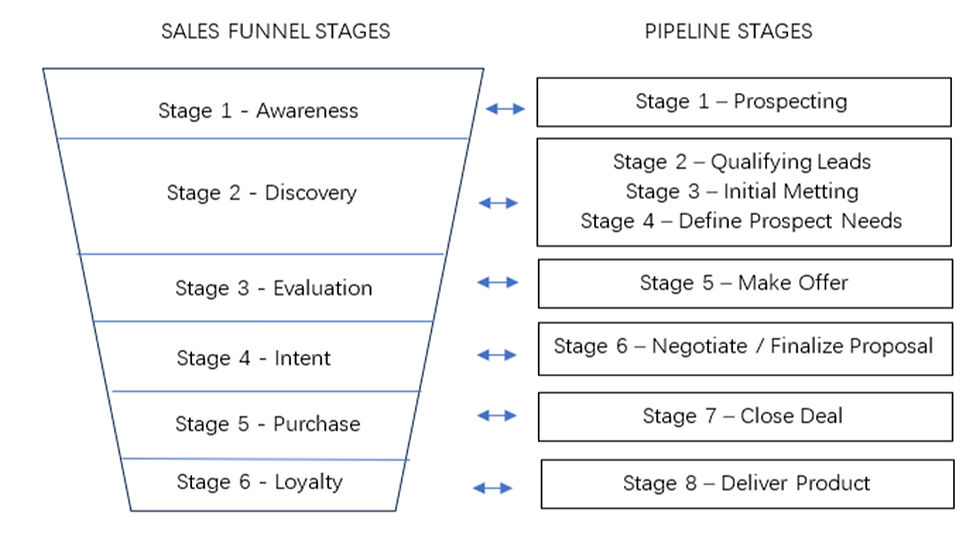
Figure 1.1 – Sales Funnel Stages with Its Corresponding Pipeline Stages
Source: Makad, n.d.
In summary, journal research since 2021 demonstrates that integrating chatbots into social media marketing can lead to positive outcomes, such as improved communication quality, enhanced user response behavior, and stronger customer-brand relationship (Vo & Nguyen, 2022); the development of long-term brand affinity and customer satisfaction (Magno & Dossena, 2023); increased lead generation through more interactive chat enggements or messaging conversations (Illescas-Manzano et al., 2021); and higher views and engagement through chat-driven CTAs (Xu et al., 2023). However, empirical measurements of views, engagement, messaging conversations, and follower growth in direct response to ManyChat use remain limited in the current academic literature. Furthermore, existing studies on the impact of chatbots have generally failed to distinguish between content flows initiated by ManyChat and those generated organically, without chatbot influence. By quantifying changes in KPIs before and after the use of ManyChat prompts in the context of MaeMagan Blogsite’s recent Facebook video and picture posts, this capstone project aims to address this gap in the literature.
3. METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Design and Scenarios
The frequency of posting videos ads and picture posts on Facebook can significantly affect engagement and reach. To avoid controllable discrepancy in the results, the researcher utilized Facebook’s post scheduling feature found in Meta Business Suite. Each day, the researcher ensured that there are at least four picture posts were scheduled at consistent times (i.e., 6:00 a.m., 11:45 a.m., 6:00 p.m., and 11:45 p.m.), along with at least two to three video ads per week.
To assess the effect of ManyChat integration on Facebook KPIs such as views, engagement, messaging conversations, and follower growth, this study employs a quasi-experimental time series design consisting of two distinct testing scenarios. These scenarios are structured around controlled, time-bound periods that isolate different uses of ManyChat on MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook content – specifically its most recent video ads and picture posts. Each scenario spans ten (10) consecutive days, ensuring consistency in observation and data collection.
Scenario 1 – Benchmark (No ManyChat Integration, Full Manual Engagement)
Dates: July 13, 2025 – July 22, 2025
Description: This period serves as the baseline for comparison. No automated tools are used. Instead, the owner of MaeMagan Blogsite will engage manually with users in the comment section and via inbox, maintaining 24/7 non-stop interaction. This establishes organic performance levels without chatbot influence.
Scenario 2 – ManyChat Integration with Automated CTAs (High-Frequent Engagement)
Dates: July 23, 2025 – August 1, 2025
Description: During this period, ManyChat’s automated responses will be used to reply to post comments and direct users to MaeMagan Blogsite via Messenger CTAs and website links. Engagement remains continuous (24/7), although Facebook-imposed restrictions (i.e., comment blocking or temporary automation limitations), may occur. The effects of high-intensity automation will be closely monitored.
Table 3.1 – Summary Table of Two Scenarios

Source: Author
The structured approach allows for comparative analysis of social media performance under varying chatbot engagement strategies. Patterns in views, likes, shares, message interactions, and follower counts will be compared across all these two scenarios to draw meaningful conclusions regarding the effectiveness and limitations of ManyChat integration.
3.2 Research Method and Hypotheses
This study adopts a quasi-experimental time series design, also known as an interrupted time series (ITS) approach. ITS is used to determine causal effects in real-world settings where randomized control trials are not feasible (Turner et al., 2021; Ewusie et al., 2020). This method involves repeated measurement of outcome variables before and during the introduction of an intervention – in this case, the ManyChat chatbot.
The independent variable is the use of ManyChat’s automated response to post comments. The dependent variables are Facebook KPIs, including:
Views (of video ads and picture posts)
Engagement, specifically:
- Comments and replies
- Reactions (like, hearts, etc.)
- Shares
Messaging conversations (initiated via Facebook Messenger)
Follower growth (net increase in page followers)
These variables are illustrated the conceptual framework in Figure 2.1. The study hypothesizes that ManyChat integration will positively affect Facebook KPIs by increasing user interaction, content visibility, and audience size. Based on this framework hypotheses are proposed and summarized in Table 3.2.
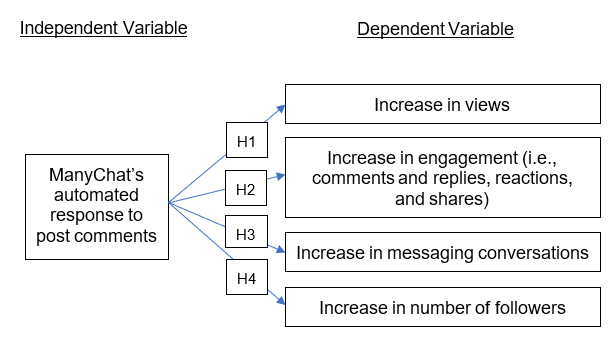
Figure 2.1 – Conceptual Framework: Independent and Dependent Variables
Source: Author
Table 3.1 – Summary of Hypotheses

Source: Author
The hypotheses will be tested across two scenarios using descriptive statistical methods to evaluate changes in the dependent variables. Results will serve as a basis for confirming or rejecting the proposed hypotheses.
3.3 Data Collection
This study employs a quantitative data collection approach using Facebook’s native analytics tool, Facebook Insights, to monitor the performance of MaeMagan Blogsite’s posts. Data will be collected over twenty (20) consecutive days, covering two ten-day phases:
1. Scenario 1 (July 13–22, 2025): No ManyChat Use; manual 24/7 engagement
2. Scenario 2 (July 23–August 1, 2025): ManyChat automation with CTAs and continuous engagement
The following KPIs will be be recorded manually and organized in spreadsheets:
Post Views
Engagement (number of comments, replies, reactions, and shares)
Messaging Conversations (number of Messenger conversations initiated)
Number of Followers (net change per day)
Efforts will be made to ensure consistency in data logging, timestamp alignment, and KPI definitions across both phases.
3.4 Data Analysis
This study uses descriptive statistical method to analyze quantitative results. The researcher will compute for frequency counts, totals, and mean values for each KPI per day. Results will be presented in tables, line graphs, and bar charts for clearer comparison across time period. By comparing the mean values, daily fluctuations, and total changes between the two scenarios, the researcher aims to determine whether a causal relationship exists between ManyChat integration and Facebook performance. Microsoft Excel will be used to process the data and generate visual aids such as line graphs and bar charts.
3.5 Justification of Research Method
The use of quasi-experimental time series design aligns with the objectives of this study, as it allows for controlled comparison between two conditions (with and without ManyChat intervention) over time. This approach makes it possible to introduce measurable changes in ManyChat use as independent variable, compare performance indicators (Facebook KPIs) before and during intervention, and test hypotheses through structured, time-based observation. This level of design rigor not only strengthens the validity of findings but also enhances the relevance of the study both academic and practical application in digital marketing.
3.6 Data Integrity and Limitations
The researcher will ensure data accuracy by maintaining consistency in tracking methods, timestamp recording, and KPI measurement. However, some external variables such as fluctuations in user activity due to bad weather conditions, changes in Facebook algorithm, temporary page restrictions or automation blocks, and/or third-party interactions or unexpected technical issues may affect the results. These limitations will be acknowledged during the analysis and discussion stages of the study.
4. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
This chapter presents the comparative analysis of Facebook key performance indicators (KPIs) before and after the integration of ManyChat on MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook page. Two ten-day experimental scenarios were analyzed in this study:
Scenario 1: Manual engagement without ManyChat (July 13–22, 2025)
Scenario 2: Automated engagement using ManyChat (July 23–August 2, 2025)
Appendix IV summarizes the quantitative data gathered from MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook Insights which are available in the Professional dashboard. Using the raw data found in Appendix II, the following sub-sections will focus on presenting, analyzing, and discussing differences observed in views, engagement (comments and replies, reactions, and shares), messaging conversations, and follower growth across these two scenarios. (See Appendix I – Quantitative Data Gathered from MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook Insights)
4.1 Results and Analysis
4.1.1 Post Views
In the context of Facebook analytics, views refers to the number of times video ads, reels, picture posts, or text content were displayed in users’ feeds and stories. Table 4.1 presents a summary of daily views, total views, and the mean (x̄) views per day recorded under both Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat integration).
Table 4.1 – Summary of Daily Views, Total Views, and Mean Views per Day in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2

Source: Author
Creating a line graph is one of the most effective ways to simplify the presentation and analysis of complex data in a time-series quasi-experimental study. In addition to clearly illustrating how values change from day by day, a line graph makes it easier to identify patterns and anomalies that may have occurred before and after the chatbot intervention. With this in mind, a visual presentation of daily view trends across the 20-day observation period is presented in Figure 4.1.
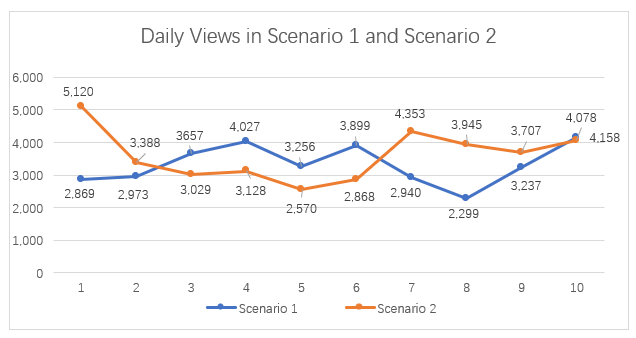
Figure 4.1 – Daily Views in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
Source: Author
Notably, on July 23, 2025, the first day of ManyChat integration, daily views peaked at 5,120, the highest recorded during the study. This spike can be attributed to the initial implementation of automated comment replies and call-to-action (CTA) links, which likely amplified content visibility through rapid and responsive engagement. However, from July 24 to July 28, a consistent decline in views was observed – dropping to 3,388, 3,029, 3,128, 2,570, and 2,868 respectively. Corresponding with this decrease, De Vera-Ruiz (2025) reported that the Philippines experienced three cyclones including Tropical Storm Crising, Tropical Storm Dante (Francisco), and Typhoon Emong (Co-may) between July 16 to 26. These severe weather conditions may have contributed to the decline in views, engagement, messaging conversations, and follower growth, likely due to flood, power interruptions, and poor Internet connectivity during the affected period.
Figure 4.2 demonstrates that the integration of ManyChat’s automated response system on MaeMagan Blogsite led to a notable improvement in Facebook post visibility and reach. Specifically, the total number of views observed during the 10-day intervention period (Scenario 2) significantly exceeded those recorded during the manual engagement phase (Scenario 1). The increase in mean (x̄) daily views by 287.1, or approximately 8.6%, indicates that the use of automated comment responses and call-to-action (CTA) links positively influenced user exposure to the content. This result supports the effectiveness of chatbot-assisted engagement in enhancing the performance of social media campaigns.
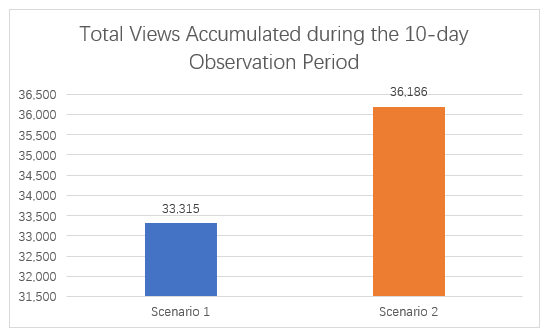
Figure 4.2 – Comparison between Scenario 1 and Scenario 2: Total Views Accumulated during the 20-day Observation Period
Source: Author
4.1.2 Engagement
Engagement, also referred to as user interactions, encompasses the number of replies or comments, reactions, shares, and saves on video ads, reels, picture posts, or text content displayed in users’ feeds and stories. To accurately measure the effects of ManyChat intervention on MaeMagan Blogsite’s posts engagement, the following sub-section highlights specific interaction metrics --- namely, comment and replies, reactions (such as likes and hearts), and post shares.
4.1.2.1 Comment and Replies
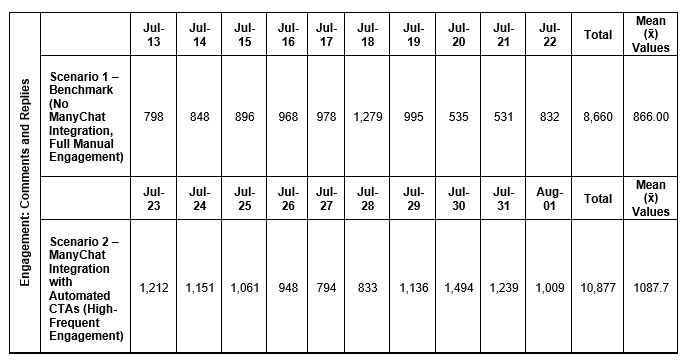
Comment and replies are key metrics in Facebook insights that refers to the number of user interactions in the form of comments and replies on video ads, reels, picture posts, and text posts displayed in users’ feeds and stories. Table 4.2 presents a summary of the daily counts, total number, and mean (x̄) of comments and replies per day as recorded under both Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat integration).
Table 4.2 – Summary of Daily Comments and Replies, Total Comments and Replies, and Mean Comments and Replies per Day in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
Source: Author
Figure 4.3 illustrates the day-by-day trend of comments and replies recorded on MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook posts during the 20-day observation period, divided into two phases: Scenario 1 (Manual Engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat Integration). From the graph, it is evident that the number of comments and replies in Scenario 2 generally exceeds those observed in Scenario 1. The line representing Scenario 2 shows a noticeable upward trend on several days, with sharp spikes particularly on July 23 and July 30, suggesting periods of heightened engagement likely triggered by the chatbot’s automated responses. In contrast, the line representing Scenario 1 shows a relatively steady but moderate level of engagement, with minor fluctuations such as a major spike on July 18. While engagement was consistent during the manual engagement phase, it lacked the intensity and frequency of interaction seen during the chatbot intervention.

Figure 4.3 – Daily Comments and Replies in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
Source: Author
The line graph visually confirms that the implementation of ManyChat was associated with an increase in comment and reply activity, reinforcing the hypothesis that chatbot automation can enhance post-level engagement on Facebook. Supporting this visual trend, the data in Table 4.2 indicates a noticeable increase of 221.7 comments and replies per day in Scenario 2, representing 25.6% rise in user engagement in the form of dialogue under posts. This suggests that the ManyChat automation likely encouraged more interactions by prompting acknowledging and responding to user inputs. Figure 4.4 summarizes the total number of comments and replies accumulated during the 20-day observation period.

Figure 4.4 – Comparison between Scenario 1 and Scenario 2: Total Comments and Views Accumulated during the 20-day Observation Period
Source: Author
4.1.2.2 Reactions (i.e., likes, hearts, etc.)
Reactions are key metrics in Facebook insights that refers to the number of reaction buttons received by the video ads, reels, picture posts, and text posts displayed in users’ feeds and stories. These reaction buttons includes Like, Love , Haha, Sad, and Angry. Table 4.3 presents a summary of the daily counts, total number, and mean (x̄) of reactions per day as recorded under both Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat integration).
Table 4.3 – Summary of Daily Reactions, Total Reactions, and Mean Reactions per Day in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2

Figure 4.5 illustrates the daily fluctuations in user reactions --- such as likes, hearts, and other emotive responses --- recorded on MaeMagan Blogsite’s Facebook page over a 20-day period, segmented into two distinct engagement strategies. In Scenario 1, which employed full manual engagement, the number of reactions remained relatively consistent, with slight variations across the 10-day period. In contrast, Scenario 2, which involved the integration of ManyChat’s automated responses and call-to-action (CTA) features, exhibited a slight upward trend in daily reactions.
Although increase in daily reactions under Scenario 2 was not as pronounced as in other engagement metrics (i.e., comments or messaging conversations), the data nonetheless indicates a positive impact of chatbot automation. The use of ManyChat appears to have sustained or modestly increased user sentiment and responsiveness, as evidenced by the higher average number of reactions per day compared to the baseline scenario. The line graph also reflects intermittent dips and peaks, which may suggest sensitivity to external variables such as content type or algorithmic restrictions during the automation period.

Figure 4.5 – Daily Reactions in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
Source: Author
Figure 4.6 presents a comparative summary of user reactions --- such as likes, hearts, and other emotive responses --- collected over the two 10-day periods in Scenario 1 and 2. The chart reveals that Scenario 2 (ManyChat Integration) generated a total 6,185 reactions, compared to 5,745 reactions in Scenario 1 (Manual engagement). This marks an increase of 440 reactions, or a 7.7% improvement following the ManyChat integration. The daily mean also reflects a positive trend: reactions rose from 574.5 per day in Scenario 1 to 618.5 per day in Scenario 2. While the increase is modest compared to comments and replies, it still demonstrates that chatbot automation contributed to slightly higher emotional engagement with MaeMagan Blogsite’s content.
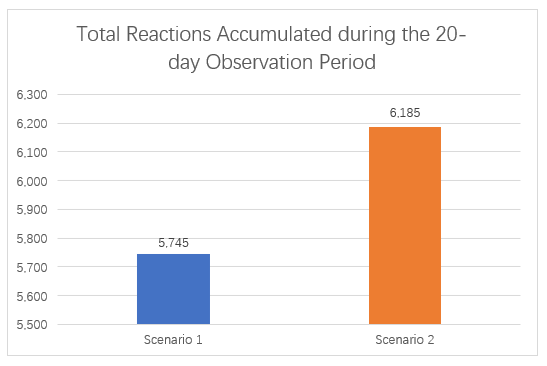
Figure 4.6 – Comparison between Scenario 1 and Scenario 2: Total Reactions Accumulated during the 20-day Observation Period
Source: Author
Overall, this finding suggests that automated engagement tools may not only drive interactions in the form of replies but also subtly enhance user sentiment and content appreciation, as reflected in the increased reactions. However, the relatively small percentage gain also implies that while ManyChat enhances engagement, it may have a stronger effect on interactive metrics (comments, messages) than on passive metrics like reactions.
4.1.2.3 Shares
Shares refers to the number of times video ads, reels, picture posts, and text posts were shared by users. In practices, users can share this content across various social media platforms, including Facebook feeds, groups, channels, Messenger, and Stories, Threads, Instagram, WhatsApp, X (formerly Twitter), and e-mail. Table 4.4 summarizes the daily number of shares, total shares, and the mean shares per day observed in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2.
Table 4.4 – Summary of Daily Shares, Total Shares, and Mean Shares per Day in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2

Source: Author
Figure 4.7 illustrates the daily number of post shares recorded during the 20-day observation period under Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat integration). A noticeable peak in shares occurred on July 16 in Scenario 1, suggesting that a specific post on that day resonated strongly with the audience. However, this was followed by a sudden decline in shares between July 20 to 22, indicating potential variability in content relevance or user interest.
In Scenario 2, share activity remained generally stable compared to Scenario 1, showing no significant increase despite the introduction of ManyChat’s automated comment responses and CTA prompts. This suggests that while chatbot automation may effectively enhance other engagement metrics --- such as comments and reactions --- it has minimal to no measurable impact on users’ propensity to share content. The findings reinforce the idea that content sharing behavior is likely driven more by content quality, relevance, or emotional resonance rather than by the presence of automated interaction tools.
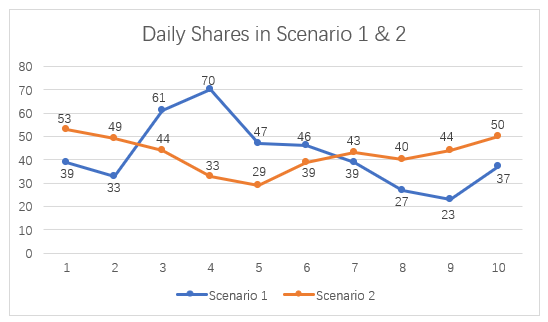
Figure 4.7 – Daily Shares in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
Source: Author
Figure 4.8 presents a comparative analysis of the total number of shares accumulated in Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat integration) across the 20-day observation period. The data reveals only a marginal difference: 422 shares were recorded in Scenario 1, while 424 shares were recorded in Scenario 2 --- an increase of merely 0.5%.
This negligible difference suggests that the use of ManyChat’s automated responses and call-to-action (CTA) prompts had little to no impact on users’ likelihood to share content. Unlike other engagement metrics such as comments or reactions, sharing appears to be less influenced by automation and more strongly affected by the content’s perceived value, emotional appeal, or personal relevance to the audience.
In summary, while chatbot integration may be effective in encouraging immediate user interaction through comments and messaging, it does not significantly influence share behavior. This insight underscores the importance of content strategy and message evidence when aiming to improve content virality on social media platforms.
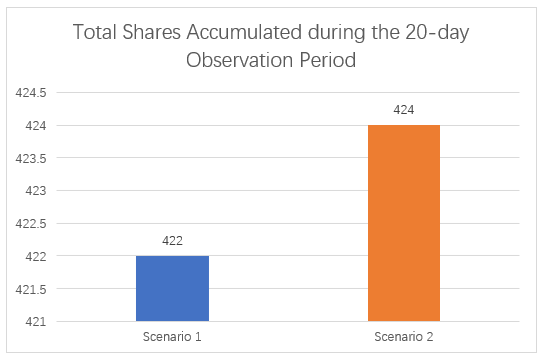
Figure 4.8 – Comparison between Scenario 1 and Scenario 2: Total Shares Accumulated during the 20-day Observation Period
Source: Author
4.1.3 Messaging Conversations
Messaging conversations refers to the number of times people messaged MaeMagan Blogsite for the first time or at least 7 days of inactivity. Table 4.5 summarizes daily number of messaging conversations, total messaging conversations, and the mean messaging conversations per day observed in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2.
Table 4.5 – Summary of Daily Messaging Conversations, Total Messaging Conversations, and Mean Messaging Conversations per Day in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
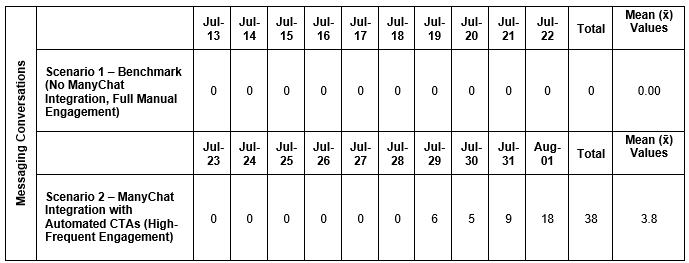
Source: Author
Figure 4.9 illustrates the number of messaging conversations initiated per day under both Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat intervention) over the 20-day observation period. As shown in Figure 4.9, there were no messaging conversations recorded during Scenario 1. In contrast, Scenario 2 demonstrates a noticeable upward trend staring July 29, with conversations peaking at 18 on August 1. A total of 38 messaging conversations were generated within the 10-day period of Scenario 2, with a daily average of 3.8 conversations.
This sharp contrast confirms that the integration of ManyChat significantly influence the volume of direct message interactions. Automated call-to-action (CTA) buttons and comment-triggered responses likely played a critical role in initiating conversations with users --- an engagement behavior that was not observed at all in the manual engagement phase.
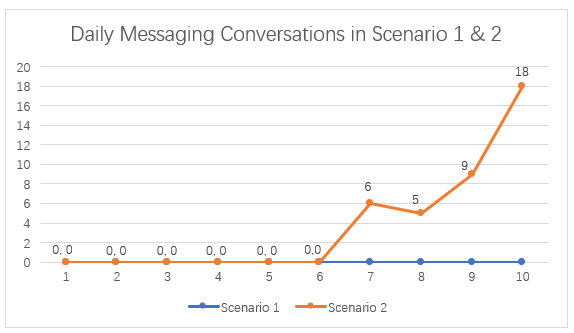
Figure 4.9 – Daily Messaging Conversations in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
Source: Author
Figure 4.10 presents a comparative summary of the total messaging conversations generated during the 20-day observation period under both Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat intervention). The chart clearly shows that zero messaging conversations were recorded during Scenario 1, confirming that manual post engagement alone did not initiate private interactions through Facebook Messenger. In contrast, Scenario 2 --- featuring ManyChat integration --- generated a total of 38 conversations. This stark contrast reinforces the impact of chatbot automation in converting public engagement into private, one-on-one interactions.

Figure 4.10 – Comparison between Scenario 1 and Scenario 2: Total Messaging Conversations during the 20-day Observation Period
Source: Author
4.1.4 Number of Total Followers
Total followers refer to number of people who follow a profile or page on Facebook. Net follower growth is calculated as the total number of new followers minus the number of people who unfollows the page. Table 4.6 summarizes the daily follower counts, total followers, and the average (mean) number of followers gained per day under both Scenario 1 and Scenario 2.
Table 4.6 – Summary of Daily Followers, Total Followers, and Mean Followers per Day in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
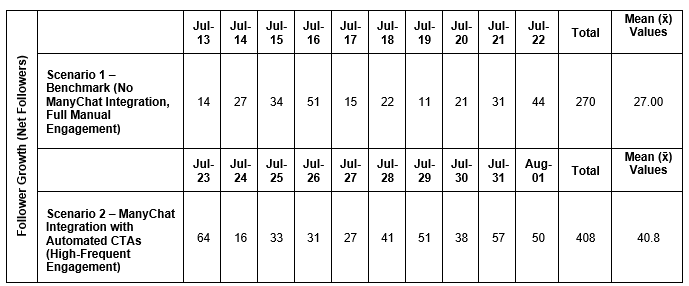
Source: Author
Figure 4.11 presents growth in daily followers in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2. In reference to this line graph, it is notable that the implementation of ManyChat in Scenario 2 resulted in a noticeable increase in follower growth compared to Scenario 1, which relied on manual engagement. The average number of net followers per day rose from 27.0 in Scenario 1 to 40.8 in Scenario 2 --- an increase of approximately 51.1%.
The highest spike in daily net followers occurred on July 23, the first day ManyChat was deployed, with 64 new followers. This suggests that the chatbot’s automated comment replies and embedded CTA links likely enhanced MaeMagan Blogsite’s page visibility and encourages users to follow the page.
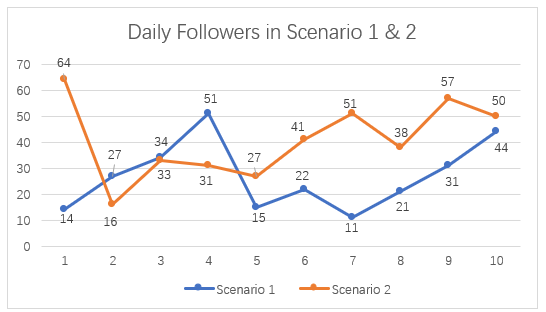
Figure 4.11 – Daily Followers Growth in Scenario 1 and Scenario 2
Source: Author
Figure 4.12 visually compares the total number of followers gained during the 20-day observation period under Scenario 1 (manual engagement) and Scenario 2 (ManyChat integration). The figure highlights a substantial increase in follower acquisition after the implementation of chatbot automation.

Figure 4.12 – Comparison between Scenario 1 and Scenario 2: Total Followers during the 20-day Observation Period
Source: Author
The results suggest that automated interactions, including time replies and CTA prompts delivered through ManyChat, effectively contributed to increased visibility and encouraged more users to follow the page. While other engagement metrics like shares showed only marginal improvements, follower growth demonstrated a stronger correlation with a chatbot-driven interaction.
4.2 Hypothesis Testing Report
Conclusions presented in section 4.2 are drawn based on the 10-day comparative data gathered from two experimental scenarios:
H1: The use of ManyChat’s automated response will significantly increase the number of views.

Data presented above shows increase in the average number of daily views during the ManyChat phase. Therefore, H1 should be accepted. To sum it up, this study suggest that automated engagement helped improve the visibility and reach of the posts.
H2: The use of ManyChat’s automated response will significantly increase post engagement including comments and replies, reactions, and shares.

Data shows significant increase in comments and reactions, while shares remained relatively stable. Overall, the total engagement improved with ManyChat. Therefore, H2 should be accepted.
H3: The use of ManyChat’s automated response will significantly increase the number of messaging conversations initiated.

Messaging conversations only occurred during the ManyChat integration phase Suggesting that automated responses and CTA-driven prompts employed in Scenario 2 were likely effective in encouraging users to initiate conversations, suggesting a direct link between the use of automated CTAs and the initiation of Messenger conversations. Overall, this finding highlights the value of chatbot automation in driving one-on-one interactions, which are essential for lead generation and customer relationship building in digital marketing. Therefore, H3 should be accepted.
H4: The use of ManyChat’s automated response will significantly increase the number of Facebook followers.

A significant increase in follower growth was observed during the ManyChat phase, supporting the idea that automated and interactive marketing contributes to building a broader audience base. Therefore, H4 should be accepted.
5. DISCUSSION
The quasi-experimental time design presented in this capstone study shows that the integration of ManyChat increased the post views by 8.6% during the 10-day automated period, suggesting that ManyChat’s automated replies and CTA links contributed to positively to post visibility and reach. Engagement such as comments and replies increased by 25.6%, indicating enhanced dialogue between the brand and users when automation was placed. ManyChat also contributed to 7.7% increase in reactions (i.e., likes, hearts, etc.), while shares showed minimal change, reinforcing that content quality may play a larger role on shares than the use of automated replies. During chatbot intervention period, messaging conversations through Facebook Messenger increased significantly from zero to 38. Followers’ growth increased by 51.1%, implying that ManyChat’s persistent engagement helped convert casual viewers into followers.
The findings align with prior studies on chatbot efficacy in digital marketing. For example, Vo and Nguyen (2022) emphasized how chatbots improve communication quality and user responsiveness, which is consistent with the rise in comments and messages observed in this study. Similarly, Magno and Dossena (2023) asserted that AI-drive interaction fosters long-term brand affinity, a likely contributor to the signficant growth in follower count. However, the study differs from Illescas-Manzano et al. (2021), who reported substantial increases in lead capture through chatbot-enhanced messaging conversations. While messaging did improve, the relatively modest number (38 conversations) suggests that in the context of real estate marketing --- where users might prefer human assistance for high-stakes inquiries --- chatbot use may be more effective for awareness-building than direct conversion. Furthermore, Xu et al. (2023) found increased engagement through chat-driven CTAs in various industries. This research partially supports their conclusion, especially in terms of reactions and comments, but the lack of signficant improvement in post shares indicates that CTA prompts alone are insufficient to drive virality in property-related content.
Despite the advantages offered by ManyChat intervention such as improved responsiveness and increased engagement, overreliance on chatbot automation may lead to unintended consequences. For instance, Facebook actively monitors for suspicious activity and enforces page restrictions to prevent spam and manipulation of engagement metrics (Nace, 2024). Furthermore, continuous automated responses may negatively affect perceived authenticity resulting to reduction in user interests to engage and interact. Therefore, online real estate marketers should implement a balanced strategy that combines automation with authentic, human-centered engagement. In doing so, online real estate marketers can avoid trigggering Facebook temporary restrictions which could potentially limit the page’s ability to comment, message, or even reach its audience organically or making the users become uninterested with the brand.
The results carry important implications for online real estate marketers operating in cost-sensitive environments. First, the integration of ManyChat allowed for continuous engagement without incurring additional manpower costs --- an advantage for small firms or independent brokers. The increase in follower count and message volume suggests that chatbot automation can play a strategic role in nurturing leads, raising brand awareness, and expanding audience reach. However, automation should carefully balance with content quality and authenticity. While ManyChat increased superficial interactions such as likes or replies, it had limited influence on deeper user actions like shares or conversions, which may depend on more persuasive content, property appeal, or time-sensitive relevance.
6. CONCLUSION, IMPLICATIONS, LIMITATIONS, AND RECOMMENDATIONS
6.1 Conclusion
This capstone study explored the integration of ManyChat’s automated messaging system into Facebook marketing strategy of MaeMagan Blogsite, with the goal of enhancing key performance indicators such as views, engagement, messaging conversations, and follower growth. By comparing manual engagement versus chatbot-enabled automation, the study demonstrated that ManyChat can significantly improve certain metrics, particularly in driving user interactions and expanding audience reach.
In conclusion, this research affirms that automation tools like ManyChat, when paired with strategic content planning and creative branding, can serve as powerful assets in building a credible and compelling online presence. As I continue to grow MaeMagan Blogsite and pursue my career in global real estate marketing, these insights will guide my digital strategies and help bridge gap between automated efficiency and human-centered communication in real estate.
6.2 Implications of the Study
These findings carry important implications not only for social media strategy but also for my broader vision of becoming a globally recognized online real estate marketer. The improvements observed in engagement and follower growth suggest that with the right tools and strategies such as chatbot automation, well-timed content, and clear call-to-action prompts, creative real estate content can reach a wider audience, foster deeper engagement, and ultimately drive more users to platforms like www.maemagan.com.
The study also reveals the importance of balance. While automation can enhance efficiency and responsiveness, excessive reliance on tools like ManyChat may trigger platform restrictions, particularly if engagement patterns appear unnatural or spam-like. In addition, meaningful engagement in real estate still relies on content quality, storytelling, and authenticity; areas where creative work remains essential.
6.3 Limitations and Recommendations for Future Study
Overall, the study is not without limitations. First, due to short time frame available to complete the capstone project, only a 20-day observation period was included. A limited observation period may not fully capture accurate long-term engagement patterns, including delayed user responses. Second, the findings of this study are specific to Facebook; therefore, the results may not be applicable to other social media platforms such as Instagram or YouTube, where user behavior and chatbot integration may differ. Third, uncontrollable external factors such as adverse weather conditions in the Philippines, changes in Facebook’s algorithm, and platform-imposed restrictions may have influenced the outcomes. Fourth, this study did not explore user sentiment or satisfaction with chatbot interactions. To address these limitations, future research should incorporate both quantitative data and qualitative insights. Conducting surveys or interviews could provide a deeper understanding of the effectiveness of AI-driven customer engagement. Another recommendation is to extend the observation period, as a longer timeframe would better capture sustained engagement trends and user behavior over time.
REFERENCES
Cheng, X., Bao, Y., Zarifis, A., Gong, W., & Mou, J. (2021). Exploring consumers response to text-based chatbots in e-commerce: The moderating role of task complexity and chatbot disclosure. Internet Research, 32(2), 496-517, https://doi.org/10.1108/INTR-08-2020-0460.
DeVera-Ruiz, E. (2025, July 27). Philippines may remain cyclone-free until end of July; 'habagat' rains to persist over western Luzon. Retrieved from Manila Bulletin: https://mb.com.ph/2025/07/27/philippines-may-remain-cyclone-free-until-end-of-july-habagat-rains-to-persist-over-western-luzon
Ewusie, J., Soobiah, C., Blondal, E., Beyene, J., Thabane, L., & Hamid, J. (22020). Methods, Applications and Challenges in the Analysis of Interrupted Time Series Data: A Scoping Review. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, 13, 411-423, https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S241085.
Grandinetti, J. (2023). Examining embedded apparatuses of AI in Facebook and TikTok. AI & Society, 38(4), 1273-1286, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-021-01270-5.
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M., Singh, R., & Suman, R. (2022). Artificial intelligence (AI) applications for marketing: A literature-based study. International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 3(2022), 119-132, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijin.2022.08.005.
IBM. (2021, October 15). What is a chatbot? Retrieved from IBM: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/chatbots
Illescas-Manzano, M., López, N., González, N., & Rodríguez, C. (2021). Implementation of Chatbot in Online Commerce, and Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(2). 125-145, https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7020125.
Keenan, M. (2022, June 27). Your Omnichannel Guide to CTA Buttons. Retrieved from Manychat: https://manychat.com/blog/call-to-action-buttons/
Li, M., & Wang, R. (2023). Chatbots in e-commerce: The effect of chatbot language style on customers’ continuance usage intention and attitude toward brand. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 71(2023), 103209, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103209.
MaeMagan Blogsite. (2025, August 4). MaeMagan Blogsite's Facebook Page. Retrieved from https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100088925015502
MaeMagan Real Estate Blogsite. (2025, August 4). Home Page. Retrieved from MaeMagan Real Estate Blogsite: https://www.maemagan.com/
Magno, F., & Dossena, G. (2023). The effects of chatbots’ attributes on customer relationships with brands: PLS-SEM and importance–performance map analysis. The TQM Journal, 35(5), 1156-1169, https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-02-2022-0080.
Makad, S. (n.d.). Build a Sales Funnel and Enhance your Business Profits in 6 Easy Steps. Retrieved from Growth Hackers: https://www.growth-hackers.net/build-a-sales-funnel-enhance-business-profits-steps/
Meghashilpa, R., & Suresh, B. (2024). The Evolution of Real Estate: Digital Marketing's Influence. REST Journal on Banking, Accounting and Business, 3(4), 21-28, : https://doi.org/10.46632/jbab/3/4/4.
Nace, T. (2024, February 26). How To Check For Account Restrictions On Facebook. Retrieved from YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VID43_1HdCc&t=59s
Quesenberry, K. (2024). Social Media Strategy: Marketing, Advertising, and Public Relations in the Consumer Revolution (4th Edition). Lanham: Rowman & Littlefield.
Turner, S., Karahalios, A., Forbes, A., Taljaard, M., Grimshaw, J., & McKenzie, J. (2021). Comparison of six statistical methods for interrupted time series studies: empirical evaluation of 190 published series. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 21, 134, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-021-01306-w.
Vo, H., & Nguyen, K. (2022). Understanding the Effects of Chatbot Marketing Efforts on Customer-Brand-Relationship: A Case Study of Young Users of Facebook Messenger in Vietnam. European Modern Studies Journal, 6(6), 36-53.
Weinberg, G., & Mares, J. (2015). Traction: How Any Startup Can Achieve Explosive Customer Growth. New York: Portfolio/Penguin.
Xu, Y., Chen, W., & Ow, T. (2023). The effec of social media posts’ characteristics on customer engagement: Evidence from WeChat. Information & Management, 60(7), 103854, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2023.103854.
Comments